What Is Hangxiety?
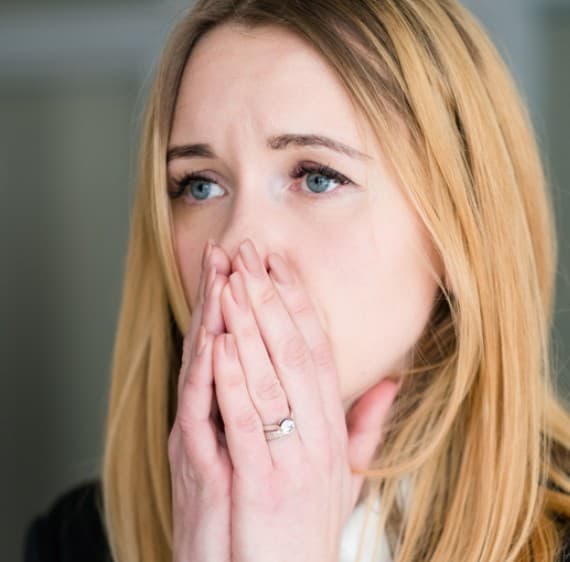

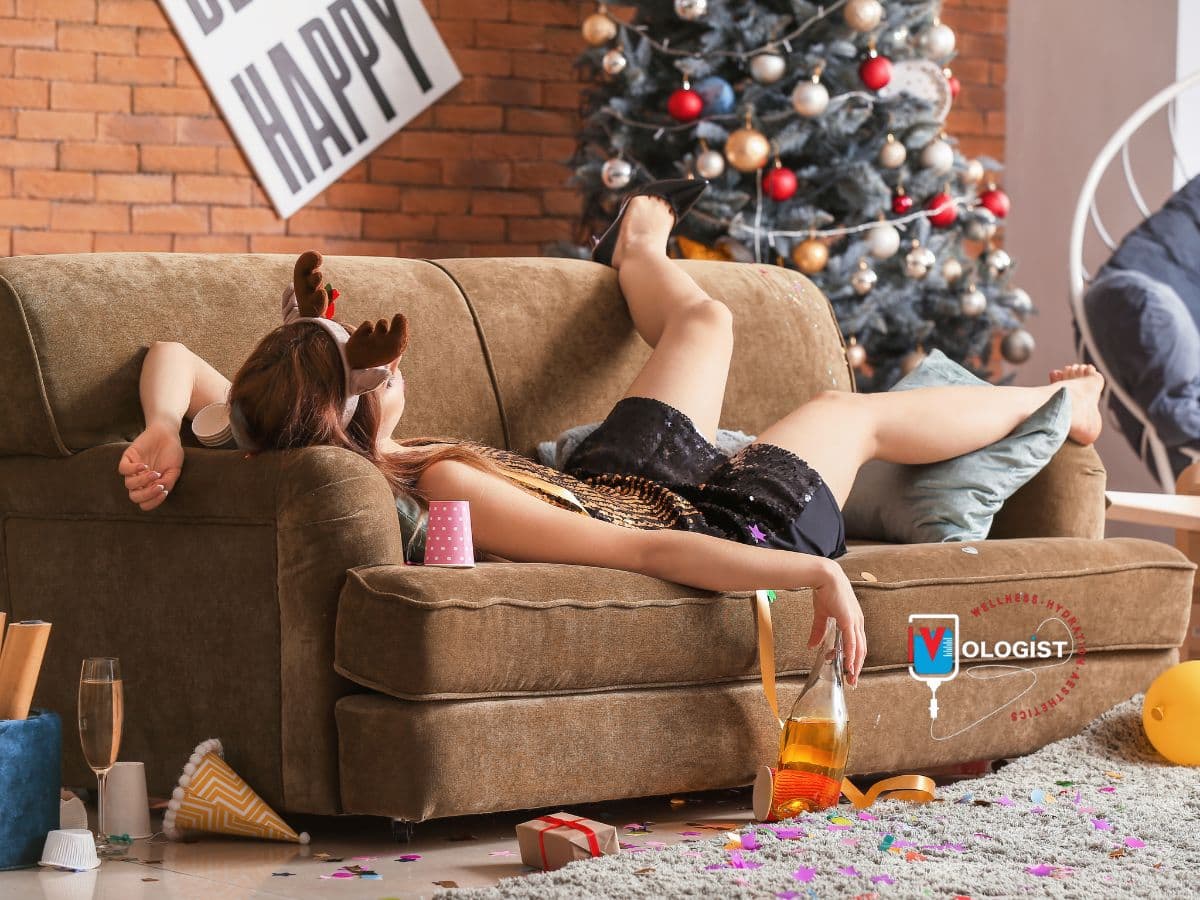
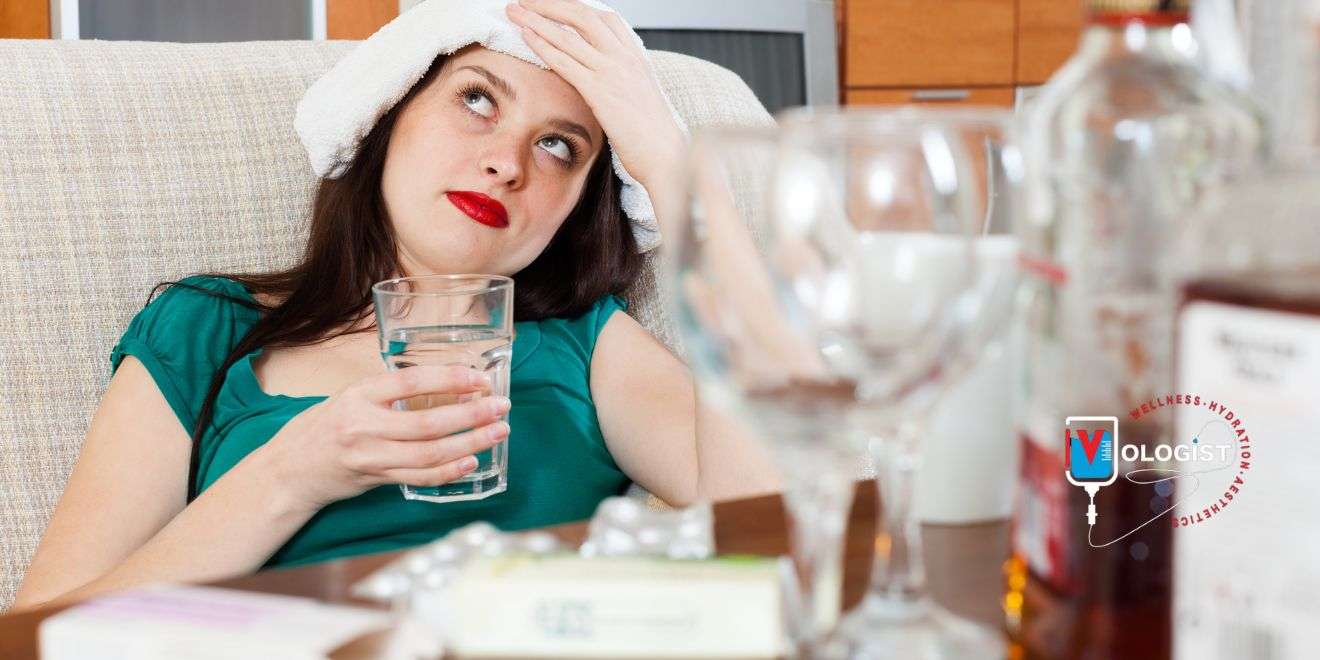
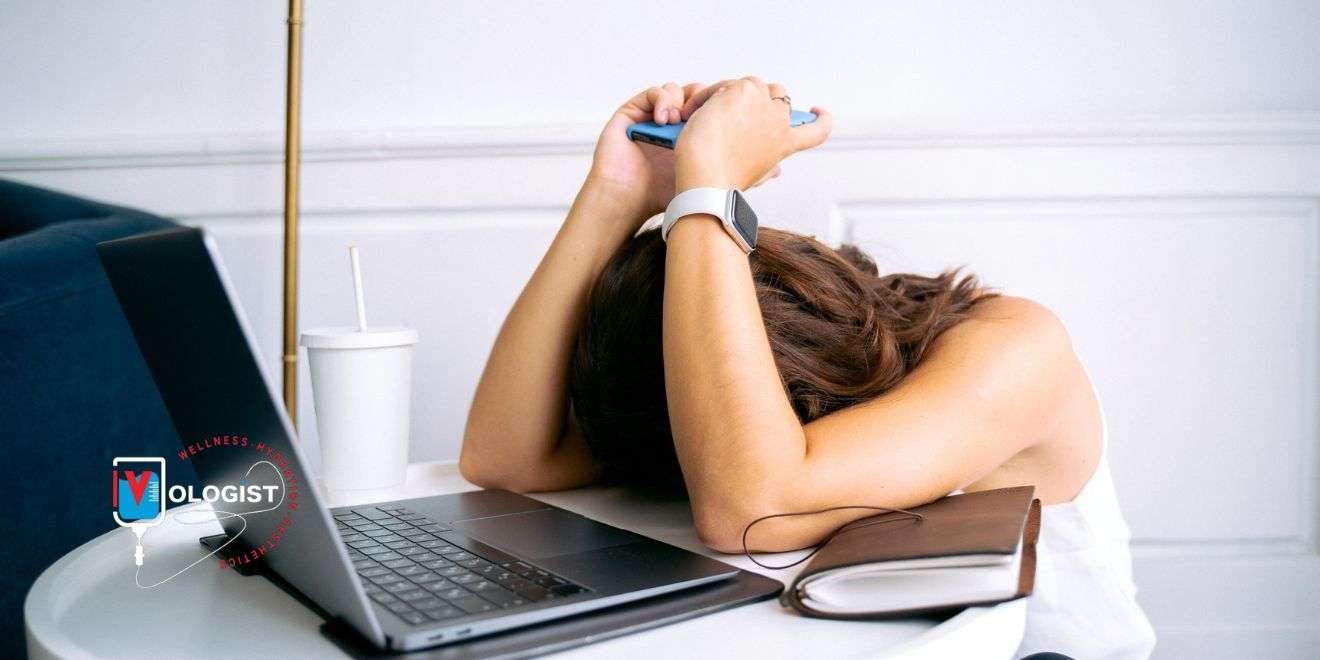
What is hangxiety? Have you ever experienced that irritable, anxious feeling in the morning after a night of drinking? If so, you may have experienced “hangxiety,” a colloquial term used to describe the unease that accompanies a hangover. It’s a sensation that many of us know all too well, yet few of us like to talk about. Hangxiety is a real phenomenon characterized by heightened nervousness, restlessness, and a general sense of uneasiness. It’s an unwelcome companion to the physical symptoms of hangover, like dehydration, headache, and fatigue. Not everyone experiences hangxiety, but for those who do, it can be rather unpleasant.
The term “hangxiety” is a combination of “hangover” and “anxiety,” reflecting the psychological discomfort that can accompany the physical symptoms of a hangover. There are several factors that may contribute to hangxiety:
Dehydration: Alcohol is a diuretic, leading to increased urine production and dehydration. Dehydration can contribute to feelings of anxiety.
Neurotransmitter Changes: Alcohol affects neurotransmitters in the brain, including gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate. These changes can influence mood and contribute to anxiety.
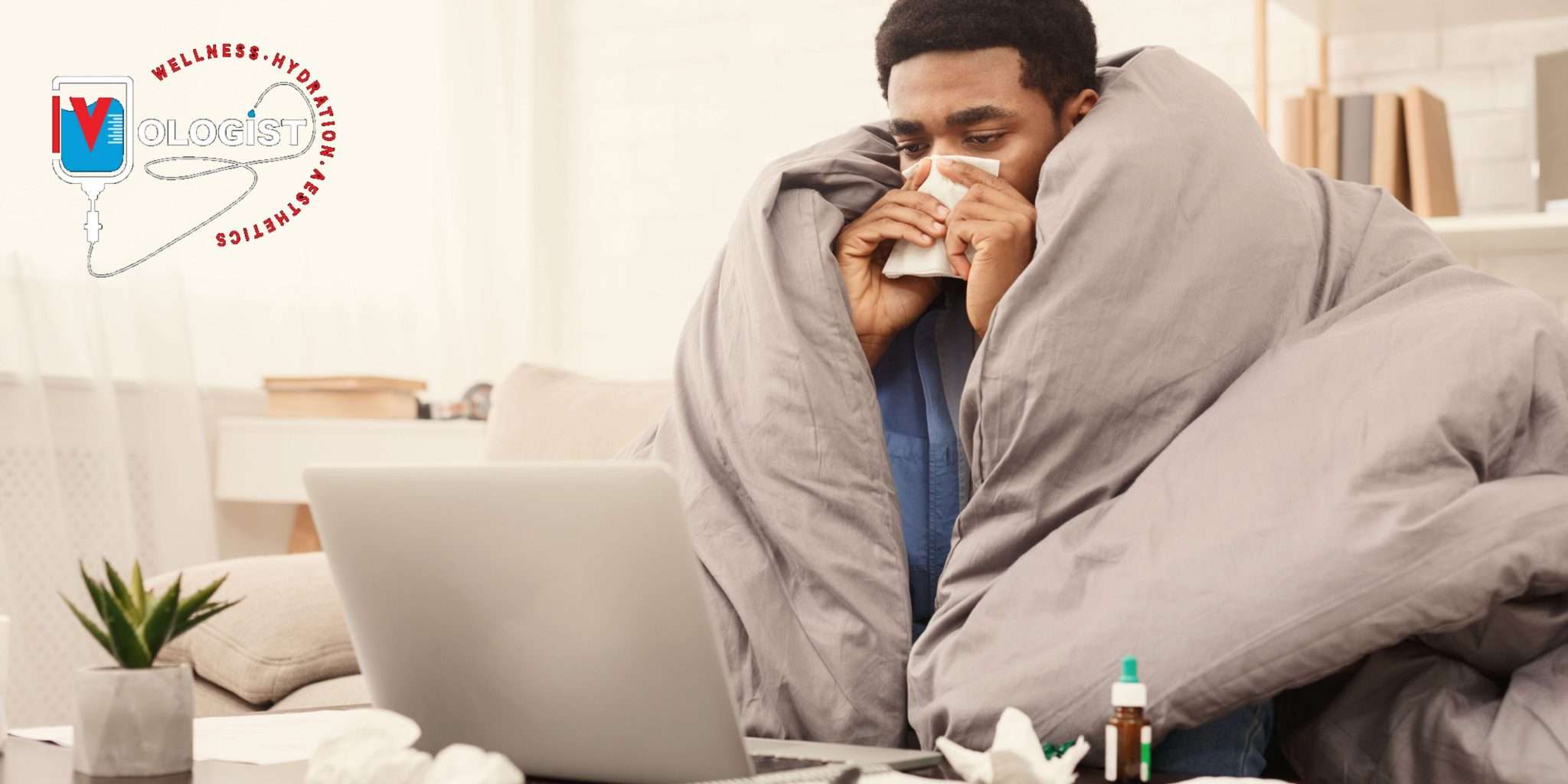
Disrupted Sleep: Alcohol can interfere with sleep patterns, leading to poor-quality sleep. Lack of sleep is associated with increased anxiety.
Withdrawal: As alcohol leaves the system, it can lead to a temporary withdrawal effect, contributing to feelings of unease.
Regret or Guilt: Actions or decisions made while under the influence of alcohol may lead to feelings of regret or guilt, contributing to anxiety.
Should you awake from a night of drinking with the symptoms of hangxiety, there are several things you can do for some much-needed relief.