What Is Compounded Semaglutide?

When exploring weight-loss treatments or managing type 2 diabetes, compounded Semaglutide is often a term that comes up. For individuals considering this option, it’s crucial to understand what compounded Semaglutide is, how it works, and how it compares to brand-name alternatives. Additionally, tools like a compounded Semaglutide dosage chart play an important role in ensuring safe and effective use.
Understanding Compounding and Its Role
Compounding refers to the process of creating custom medications by combining, mixing, or altering ingredients to meet the specific needs of a patient. Compounded Semaglutide is produced in specialized pharmacies, often addressing specific requirements such as allergen-free formulations or lower costs. For patients seeking weight-loss medications outside of brand-name versions like Ozempic or Wegovy, compounded options can provide a more affordable alternative.
- Affordability: Compounded Semaglutide typically costs less than its FDA-approved counterparts, making it a viable option for those paying out-of-pocket.
- Accessibility: Compounded formulations can sometimes bypass supply chain shortages, providing treatment to those unable to access brand-name options.
How Semaglutide Works
Semaglutide belongs to a class of medications called GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs mimic the effects of a natural hormone that helps regulate appetite, insulin production, and blood sugar levels. Here’s how it works:
- Appetite Control: Semaglutide signals the brain to feel fuller for longer, helping individuals reduce calorie intake.
- Insulin Sensitivity: It enhances the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, which is particularly important for managing type 2 diabetes.
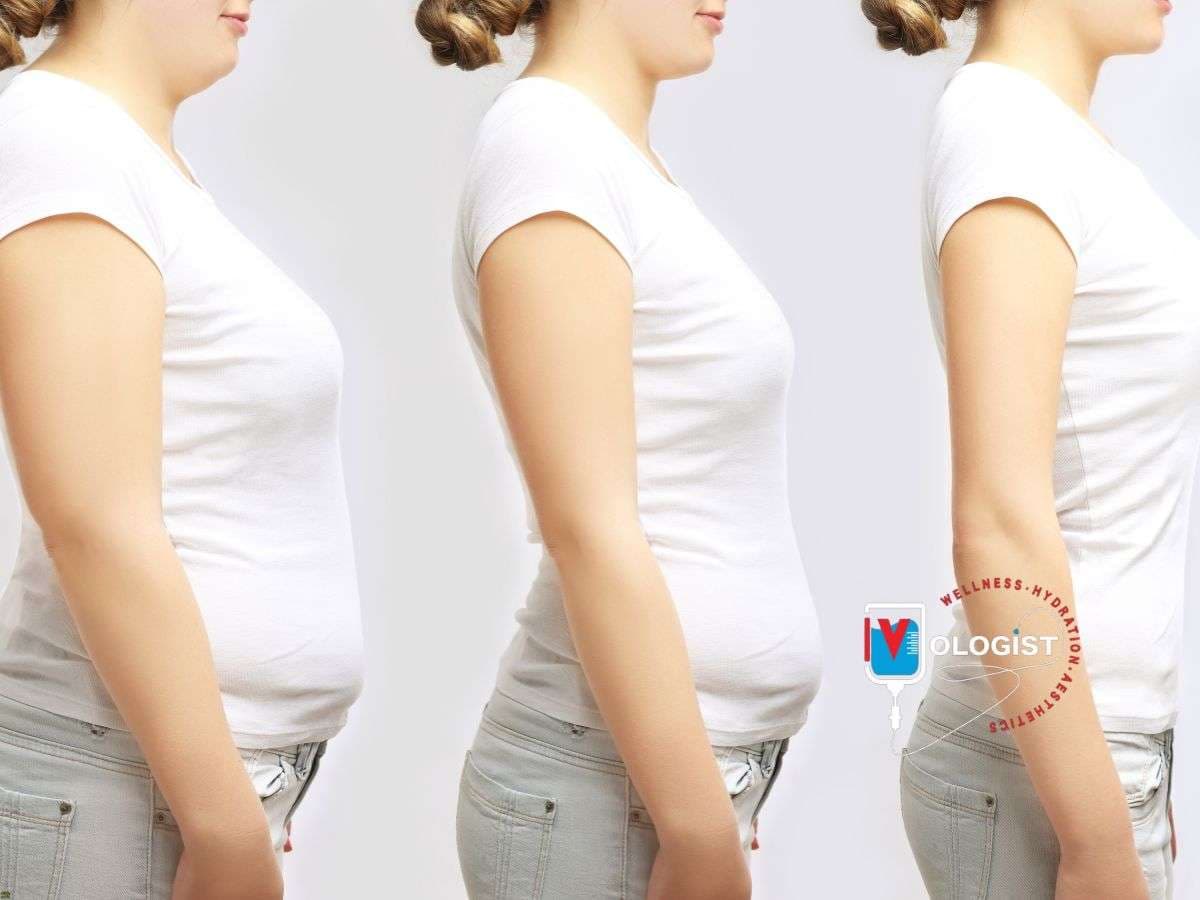
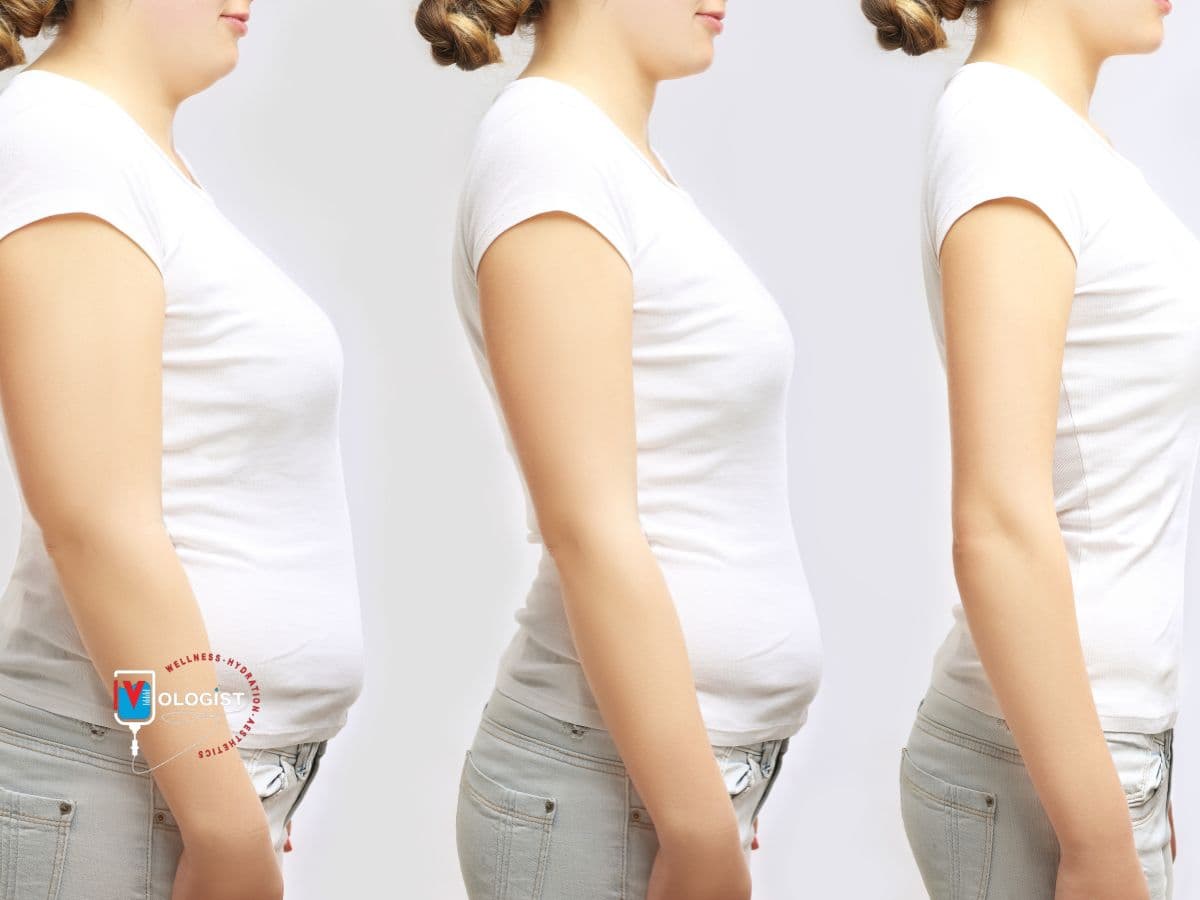
- Weight Loss: By addressing appetite and metabolism simultaneously, Semaglutide leads to significant weight-loss outcomes in many patients.
Compounded vs. Brand-Name Semaglutide
When comparing compounded Semaglutide to brand-name options like Ozempic or Wegovy, there are several key differences to consider:
- Regulation: Brand-name medications are FDA-approved, meaning they meet strict standards for safety, consistency, and efficacy. Compounded Semaglutide, however, is not FDA-regulated, raising potential concerns about quality variations.
- Cost: Compounded variations often come at a lower cost, but patients need to weigh this against the potential risks of unregulated formulations.
- Customization: Compounding allows for personalized formulas, which may not be possible with standard brand-name options.
Understanding these differences underscores the importance of accurate dosing. A compounded Semaglutide dosage chart can guide patients in adhering to proper schedules, helping to optimize results while minimizing side effects. Consulting with a healthcare provider or trusted pharmacy is essential to ensure the best outcomes.
By learning how compounded Semaglutide works and how it compares to brand-name treatments, patients can make informed decisions about their weight-loss or diabetes management plans. Always prioritize guidance from licensed professionals when navigating these choices.